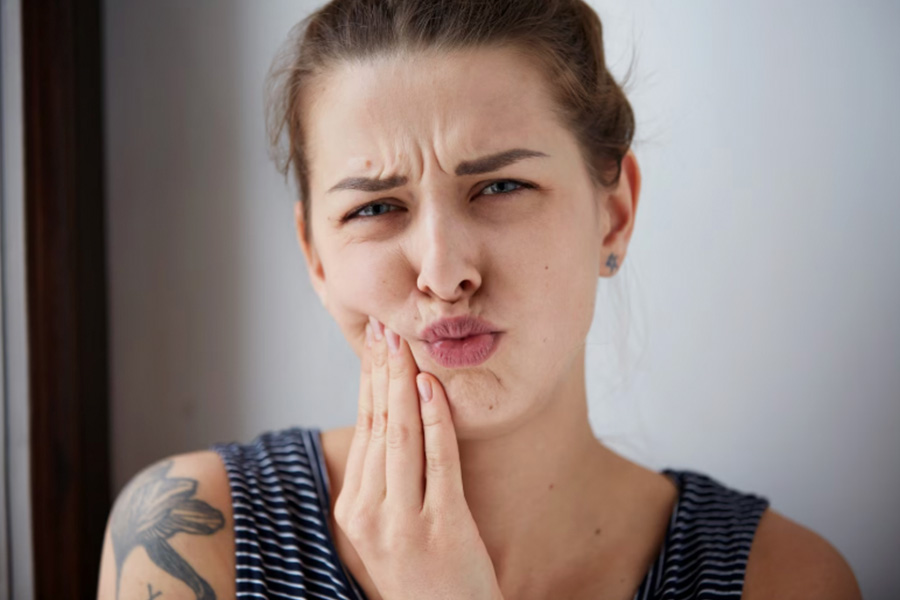
Soft tissue injuries inside the mouth, including the gums, lips, tongue, and cheeks, are more common than many people realize. They can occur due to accidents, sports injuries, biting down too hard, or even from irritation caused by braces or dental appliances. While most of these injuries are minor, some may require immediate professional care to prevent infection or long-term complications. Understanding how to manage soft tissue injuries can make all the difference in ensuring a quick recovery and protecting your overall oral health.
When these types of injuries occur, acting promptly is crucial. Managing bleeding, controlling swelling, and maintaining wound cleanliness can help prevent infection and further trauma. In severe cases, emergency dentistry services may be necessary to repair tissue damage, control excessive bleeding, or prevent potential complications that could impact your teeth and jaw alignment.
If you are looking for a professional and experienced dentist in Lake Mary, our dental team is well-equipped to handle all types of oral injuries with care and precision. We provide immediate attention for soft tissue trauma, ensuring that each patient receives gentle, effective, and timely treatment to promote proper healing.
Understanding Soft Tissue Injuries in the Mouth
Soft tissues in the mouth, the gums, tongue, lips, and inner cheeks, play vital roles in eating, speaking, and protecting the teeth. These tissues are highly vascular, meaning they have an abundant blood supply, which helps wounds heal quickly but also makes them prone to heavy bleeding when injured.
Common causes of oral soft tissue injuries include:
- Accidental biting during eating or talking
- Sports-related trauma without proper mouth protection
- Falls or collisions
- Sharp food edges or broken dental appliances
- Burns from hot food or drinks
Common Types of Soft Tissue Injuries
Mouth injuries can vary in type and severity. The most frequent include:
1. Gum Lacerations
Gums can tear or become inflamed from brushing too hard, sharp foods, or trauma from dental appliances. These wounds may expose sensitive areas, leading to pain, bleeding, and an increased risk if not treated promptly.
2. Lip Injuries
Lips can split easily due to falls or contact sports. Because the lips are rich in blood vessels, even minor cuts can cause significant bleeding. Cold compresses can help control swelling, but deeper wounds might need sutures.
3. Cheek Tears and Bites
Cheek injuries often happen when chewing too quickly or following dental procedures when the area is numb. Persistent cheek biting can lead to irritation, swelling, or infection if bacteria enter the wound.
4. Burns and Abrasions
Consuming very hot foods or beverages can cause burns to the delicate tissues inside the mouth. While these typically heal within days, severe burns may require medical attention.
Understanding the type of injury helps determine the appropriate treatment method, from simple rinsing to professional care.
First Aid for Soft Tissue Injuries
Immediate action following a soft tissue injury can significantly reduce discomfort and prevent infection. Here are the key steps to follow:
Rinse Your Mouth:
Use warm salt water to clean the area and remove debris gently. This helps reduce bacteria and supports healing.
Apply Pressure:
Use a clean gauze pad or cloth to apply gentle pressure if bleeding occurs. Hold it in place for 10–15 minutes, or until the bleeding stops.
Cold Compress:
Applying ice wrapped in a cloth can minimize swelling and soothe pain. Avoid placing ice directly on the skin or wound.
Avoid Irritants:
Refrain from eating spicy, acidic, or extremely hot foods until the area has healed completely.
Pain Relief:
Over-the-counter pain medication may be used if discomfort persists; however, follow the dosage instructions carefully.
If the bleeding doesn’t stop after 15–20 minutes or the wound appears to be deep, contact your dentist immediately for further evaluation.
When to Seek Professional Dental Care
While minor mouth injuries can often be treated at home, certain signs indicate that professional care is necessary. You should contact your dentist immediately if you experience:
- Continuous bleeding that doesn’t stop with pressure
- Deep cuts or punctures in the gums, lips, or cheeks
- Torn tissue or a visible flap of skin
- Swelling that worsens after several hours
- Severe pain or difficulty opening your mouth
- Signs of infection, such as pus, fever, or a foul taste in the mouth
In such cases, prompt dental treatment helps prevent further complications.
Professional Treatments for Soft Tissue Injuries
Dentists possess advanced tools and expertise to manage oral soft tissue injuries effectively. Depending on the severity of the wound, treatment options may include:
Cleaning and Debridement:
The dentist removes debris and disinfects the wound to prevent infection.
Suturing:
Deep or large lacerations may need stitches to close the tissue and promote healing.
Antibiotic Therapy:
If there’s a risk of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent bacterial growth.
Tetanus Booster:
For injuries caused by contaminated objects, a tetanus shot may be recommended.
Follow-up Visits:
The dentist monitors the healing process and ensures that there are no underlying issues, such as nerve or tooth root damage.
Proper professional care ensures not only healing but also aesthetic recovery, especially for visible injuries on the lips or face.
Preventing Soft Tissue Injuries
While accidents can happen unexpectedly, you can reduce your risk of oral soft tissue injuries by following preventive measures:
Wear a Mouthguard:
Especially during sports, mouthguards protect your teeth and soft tissues from impact.
Practice Caution While Eating:
Avoid chewing too fast or biting hard foods that can cause tears or cuts.
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene:
Healthy gums and tissues are less prone to injury and infection.
Be Careful with Hot Foods and Drinks:
Always test the temperature of your food and drink before consumption to avoid burns.
Regular Dental Checkups:
Routine visits help identify potential issues, such as sharp tooth edges or ill-fitting dental appliances, that could cause irritation.
Recovery and Home Care After Treatment
After receiving dental care, proper at-home care ensures faster healing and prevents complications. Here are essential tips to follow during recovery:
- Stick to soft foods for the first few days. Soups, smoothies, and yogurt are gentle on healing tissues.
- Continue rinsing your mouth with warm salt water several times a day to keep the wound clean and prevent infection.
- Avoid touching the injured area with your tongue or fingers.
- If sutures were placed, follow your dentist’s instructions on care and removal.
- Monitor the area for any signs of delayed healing or infection.
Most soft tissue injuries heal within one to two weeks with appropriate care. However, severe wounds might take longer, especially if there’s significant tissue loss or secondary infection.
Timely Care for Long-Lasting Oral Health
Soft tissue injuries to the gums, lips, and cheeks may seem minor, but they can cause significant discomfort and potentially lead to complications if left unattended. By knowing how to respond immediately and when to seek professional help, you can ensure swift recovery and maintain optimal oral health.
Prompt action, proper hygiene, and professional dental intervention when needed are the keys to preventing lasting damage. Whether the injury is caused by an accident, a sports incident, or a simple misstep, taking it seriously ensures that your smile remains healthy, pain-free, and beautiful for years to come.






Leave a Reply